Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio Formula Example Calculation Explanation
Typically, a higher fixed asset turnover ratio indicates that a company has more effectively utilized its investment in fixed assets to generate revenue. A higher ratio is generally favored as there is the implication that the company is more efficient in generating sales or revenues. A lower ratio illustrates that a company may not be using its assets as efficiently.
What is the difference between the Fixed Asset Turnover and Asset Turnover Ratio?
The fixed assets include al tangible assets like plant, machinery, buildings, etc. Manufacturing companies often favor the FAT ratio over the asset turnover ratio to determine how well capital investments perform. Companies with fewer fixed assets such as retailers may be less interested in the FAT compared to how other assets such as inventory are utilized.
How can a company improve its total asset turnover?
- The higher the asset turnover ratio, the better the company is performing, since higher ratios imply that the company is generating more revenue per dollar of assets.
- With this fixed asset turnover ratio calculator, you can easily calculate the fixed asset turnover (FAT) of a company.
- For example, a cyclical company can have a low fixed asset turnover during its quiet season but a high one in its peak season.
A company will gain the most insight when the ratio is compared over time to see trends. Hence, we use the average total assets across the measured net sales period in order to align the timing between both metrics. The Asset Turnover Ratio is a financial metric that measures the efficiency at which a company utilizes its asset base to generate sales. This article will help you understand what is fixed asset turnover and how to calculate the FAT using the fixed asset turnover ratio formula. FAT ratio is important because it measures the efficiency of a company’s use of fixed assets. This allows them to see which companies are using their fixed assets efficiently.
What is Fixed Asset Turnover Used For?
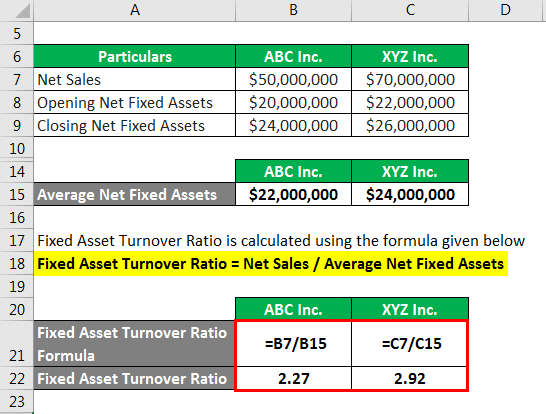
Calculate both companies’ fixed assets turnover ratio based on the above information. Also, compare and determine which company is more efficient in using its fixed assets. The asset turnover ratio is most helpful when compared to that of industry peers and tracking how the ratio has trended over time. A ratio of 1.33 means EcoGoods generates $1.33 of revenue for every $1 invested in fixed assets. This indicates moderate efficiency, but there may be room for improvement. A ratio of 2.0 means TechNova generates $2 of revenue for every $1 invested in fixed assets, indicating efficient asset utilization.
Strategies to Improve Your Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio
Hence, the best way to assess this metric is to compare it to the industry mean. At the company level, internal factors can influence asset turnover ratio. One of the prime drivers is how efficient a company is in maximizing their assets and managing inventory. The type of industry a company operates in affects its asset turnover ratio. Different industries have varying levels of capital intensity, which directly impacts how assets are used to drive revenue.
Can the fixed asset turnover be negative?
You want to ensure you’re not having liabilities outweigh assets, as this can lead to financial challenges for your business. Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. It’s always important to compare ratios with other companies’ in the industry.
A “good” ratio can vary by industry, but generally, a higher ratio indicates better efficiency. To stay on top of profitability, they will assess ways to improve efficiency, reduce costs, incentivize employees and optimize operations to maximize the bottom line. But it is important to compare companies within the same industry in order to see which company is more efficient. On Calcopolis, you can find helpful calculators for evaluating a company’s cash flow, like levered free cash flow, or the company’s profitability, like the EBITDA margin calculator.
Such ratios should be viewed as indicators of internal or competitive advantages (e.g., management asset management) rather than being interpreted at face value without further inquiry. While FACR is primarily used for business analysis, similar principles can be applied to personal finance by evaluating how efficiently personal assets are generating income. When considering investing in a company, it is important to note that the FAT ratio should not perform in isolation, but rather as one part of a larger analysis. It’s important to consider other parts of financial statements when reviewing current assets. For instance, intangible assets, asset capacity, return on assets, and tangible asset ratio.
Our in-house research team and on-site financial experts work together to create content that’s accurate, impartial, and up to date. We fact-check every single statistic, quote and fact using trusted primary resources to make sure the information we provide is correct. You can learn more about GOBankingRates’ processes and standards in our editorial policy. Remember, you shouldn’t use the FAT ratio on its own but rather as one part of a larger analysis. Diane Costagliola is a researcher, librarian, instructor, and writer who has published articles on personal finance, home buying, and foreclosure.
Outsourcing could mask underlying issues such as unstable cash flows or weak business fundamentals. The Fixed Asset Turnover (FAT) is a ratio of a company’s revenue to its fixed assets. The value of this metric reveals how well a company uses its fixed assets to generate sales. Companies with strong ratios may review all aspects that generate solid profits or healthy cash flow. FAT only looks at net sales and fixed assets; company-wide expenses are not factored into the equation. In addition, there may be differences in the cash flow between when net sales are collected and when fixed assets are acquired.
The asset turnover ratio is a financial metric that evaluates how effectively your business uses its assets to produce revenue. The fixed asset turnover ratio demonstrates the effectiveness of a company’s current fixed assets in driving sales. The higher the asset turnover ratio, the better the company is performing, since higher ratios imply that the company is generating more revenue per dollar of assets. The FAT ratio excludes investments turbotax 2014 desktop now available in working capital, such as inventory and cash, which are necessary to support sales. This exclusion is intentional to focus on fixed assets, but it means that the ratio does not provide a complete picture of all the resources a company uses to generate revenue. A higher FAT ratio indicates that a company is effectively utilizing its fixed assets to generate sales, showcasing management’s efficiency in asset utilization.
